Notes
Number Theory Basics
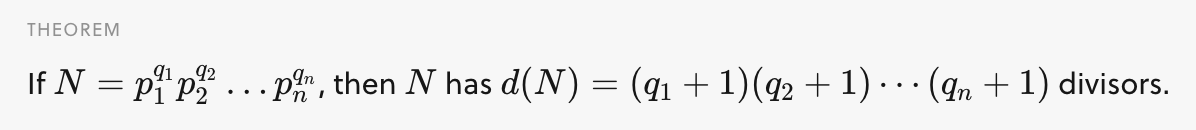

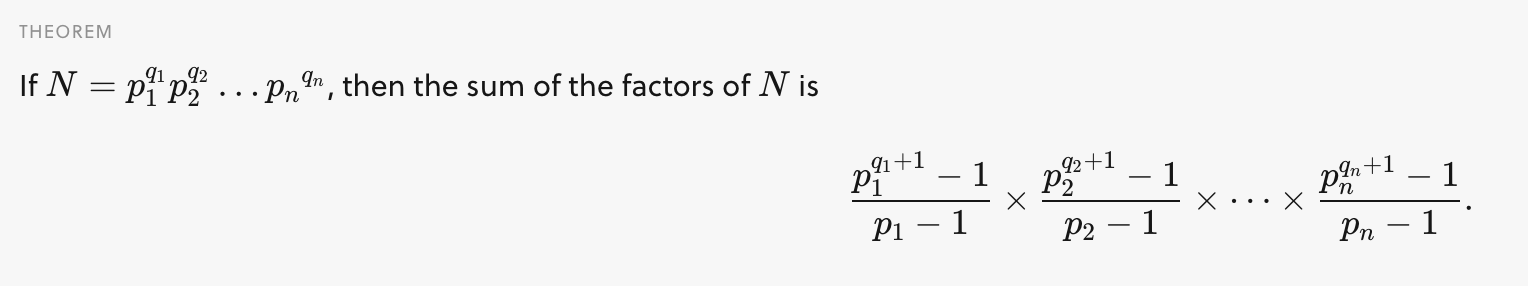

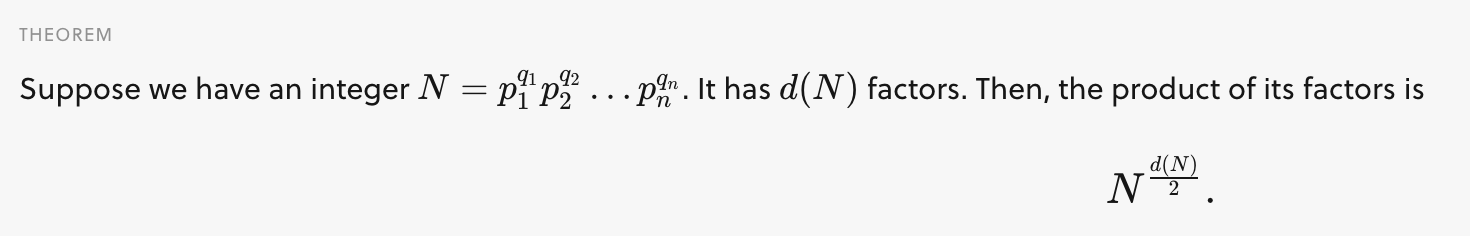

source: Factors. Brilliant.org. Retrieved 00:56, August 18, 2021, from https://brilliant.org/wiki/factors/
In number theory, Euler's totient function counts the positive integers up to a given integer n that are relatively prime to n. It is written using the Greek letter phi as φ(n), and may also be called Euler's phi function. In other words, it is the number of integers k in the range 1 ≤ k ≤ n for which the greatest common divisor gcd(n, k) is equal to 1


int n = 50;
for(int i = 1, la; i <= n; i = la + 1){
la = n/(n/i);
printf("i = %d n/i = %d la = %d\n", i, n/i, la);
}
i = 1 n/i = 50 la = 1
i = 2 n/i = 25 la = 2
i = 3 n/i = 16 la = 3
i = 4 n/i = 12 la = 4
i = 5 n/i = 10 la = 5
i = 6 n/i = 8 la = 6
i = 7 n/i = 7 la = 7 // till sqrt(n)
i = 8 n/i = 6 la = 8
i = 9 n/i = 5 la = 10 // n/j remains n/i for i ≤ j ≤ la
i = 11 n/i = 4 la = 12
i = 13 n/i = 3 la = 16
i = 17 n/i = 2 la = 25
i = 26 n/i = 1 la = 50
If for some x you have ⌊n/x⌋ = k then the greatest x' such that ⌊n/x'⌋ = k is x' = ⌊n/k⌋ because n/(n/k) = k and if you divide n by any bigger number than n/k you get a smaller quotient than k.
Checkout Linear Seive https://codeforces.com/blog/entry/54090
Mobius Function
An arithmetical function, or number-theoretic function is a complex-valued function defined for all positive integers. It can be viewed as a sequence of complex numbers.
In number theory, a multiplicative function is an arithmetic function f(n) of a positive integer n with the property that f(1) = 1 and f(ab) = f(a)f(b) whenever a and b are coprime; gcd(a, b) = 1. f(n) = f(n * 1) = f(n) f(1) hence we need the condition that f(1) = 1.
If both f(x) and g(x) are multiplicative, then h(x) = f(x)g(x) is also multiplicative.
d|n means that d can divide n (without a remainder).
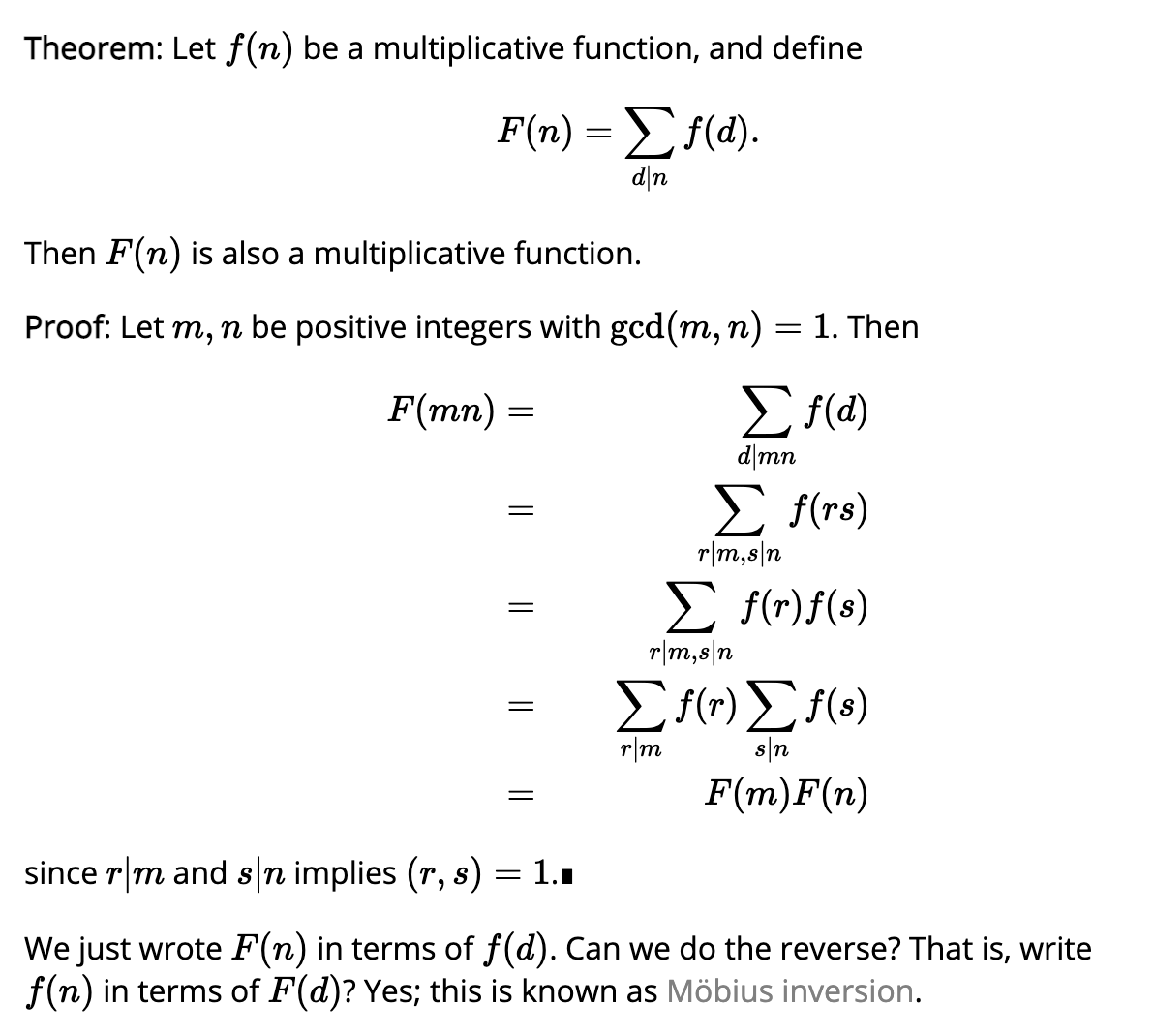


source: https://crypto.stanford.edu/pbc/notes/numbertheory/mult.html
Let's use the notation: [P] refers to the boolean expression, i.e. [P] = 1 when P is true, and 0 otherwise.
The following are multiplicative functions.
- The constant function, defined by I(n) = 1
- The identity function, defined by Id(n) = n
- Idₖ(n): The power functions, defined by
Idₖ(n) = nᵏ - Dirichlet identity, The unit function
[n = 1], 1 if n = 1 and 0 otherwise - Mobius function as defined above
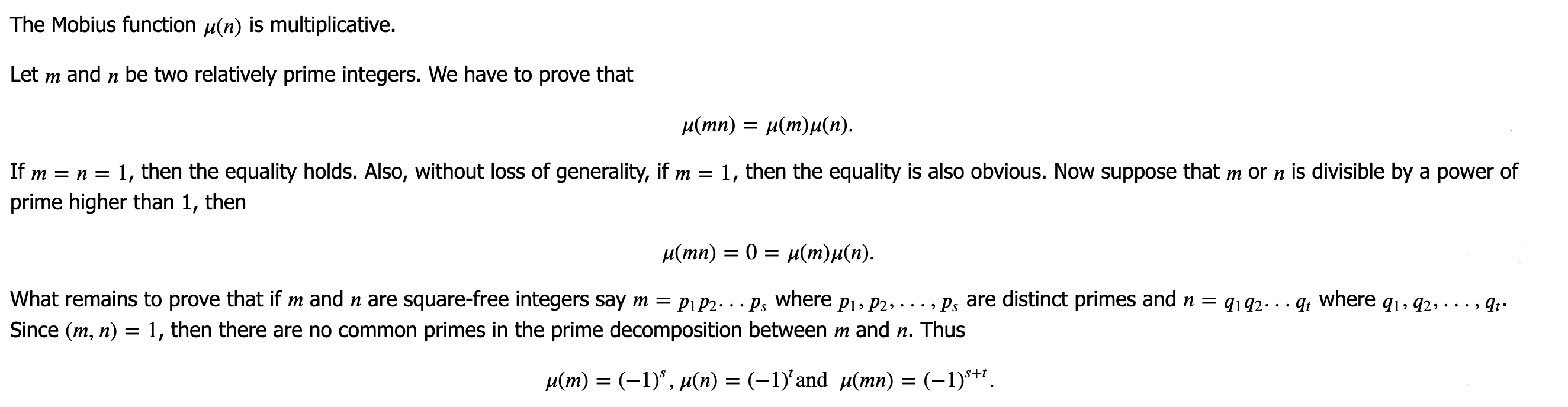
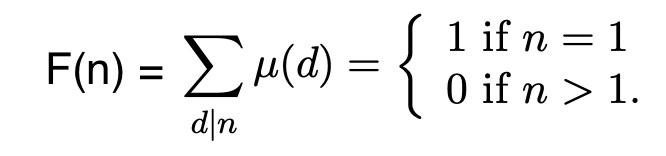
In order to prove that sum-function of mobius function is unit function, we can use the property that mobius function is multiplicative, which implies that the sum function is multiplicative and hence F(n) = F(p1^k1) F(p2^k2) ... F(pi^ki), we know that F(pi^ki) = 1 + (-1) = 0 if ki >= 1 and F(1) = 1.
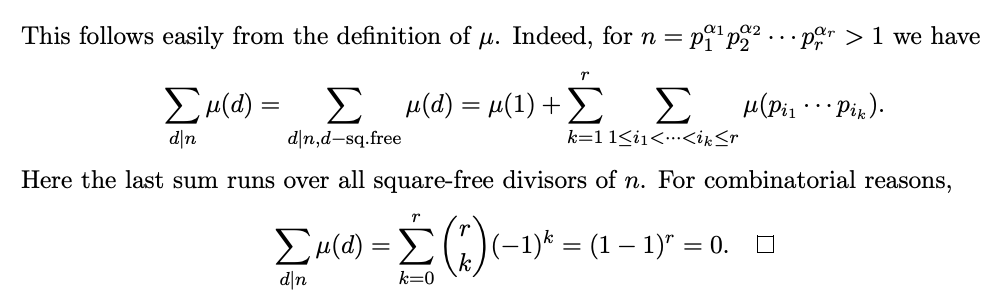
source: https://codeforces.com/blog/entry/53925
Proof using Subset parity lemma https://mathlesstraveled.com/2016/12/03/the-mobius-function-proof-part-2-the-subset-parity-lemma/
Dirichlet convolution
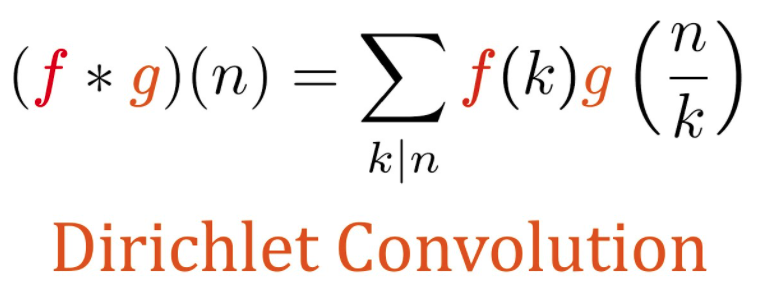
In other words, the convolution of f and g at n is the sum of f(k)g(n/k) over all positive divisors k of n.
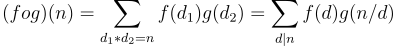
Dirichlet convolutions are
- commutative (f ∗ g = g ∗ f), and
- associative (f ∗ (g ∗ h) = (f ∗ g) ∗ h).
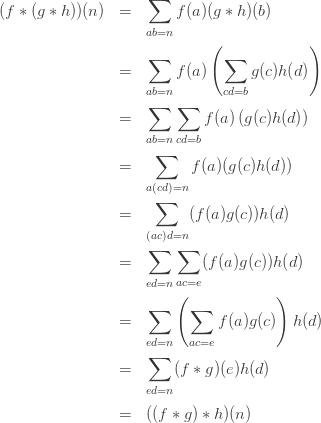
Another proof of Mobius Inversion
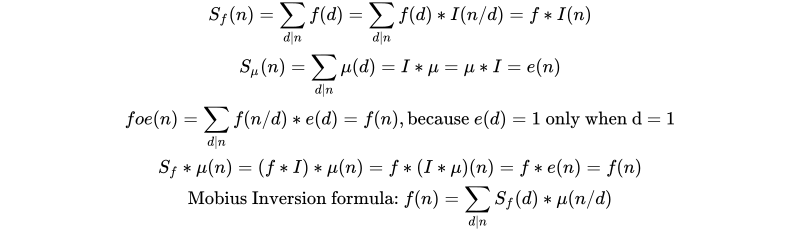
That is, Mobius function μ is the inverse of constant function I with respect to Dirichlet convolution. μ * I = ε
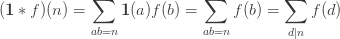
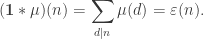
vector<int> smallest_factor;
vector<int8_t> smallest_power;
vector<int8_t> mobius;
vector<bool> prime;
vector<int> primes;
// Note: this sieve is O(n).
void sieve(int maximum) {
maximum = max(maximum, 1);
smallest_factor.assign(maximum + 1, 0);
smallest_power.assign(maximum + 1, 0);
mobius.assign(maximum + 1, 0);
prime.assign(maximum + 1, true);
mobius[1] = 1;
prime[0] = prime[1] = false;
primes = {};
for (int i = 2; i <= maximum; i++) {
if (prime[i]) {
smallest_factor[i] = i;
smallest_power[i] = 1;
mobius[i] = -1;
primes.push_back(i);
}
for (int p : primes) {
if (p > smallest_factor[i] || i * p > maximum)
break;
prime[i * p] = false;
smallest_factor[i * p] = p;
smallest_power[i * p] = smallest_factor[i] == p ? int8_t(smallest_power[i] + 1) : 1;
mobius[i * p] = smallest_factor[i] == p ? 0 : int8_t(-mobius[i]);
}
}
}
source: neal https://codeforces.com/contest/1559/submission/125955092
const int X = 2.1e5;
bitset<X> is_prime;
vector<int> pr;
vector<int> mu(X, 0);
void init() {
is_prime.flip();
is_prime[0] = is_prime[1] = false;
mu[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < X; i++) {
if (is_prime[i]) {
pr.push_back(i);
mu[i] = -1;
}
for (int p: pr) {
if (i * p >= X) break;
is_prime[i * p] = false;
if (i % p == 0) {
mu[i * p] = 0;
} else {
mu[i * p] = -mu[i];
}
if (i % p == 0) break;
}
}
}
source: ksun48 https://codeforces.com/contest/1559/submission/125949764
Problems
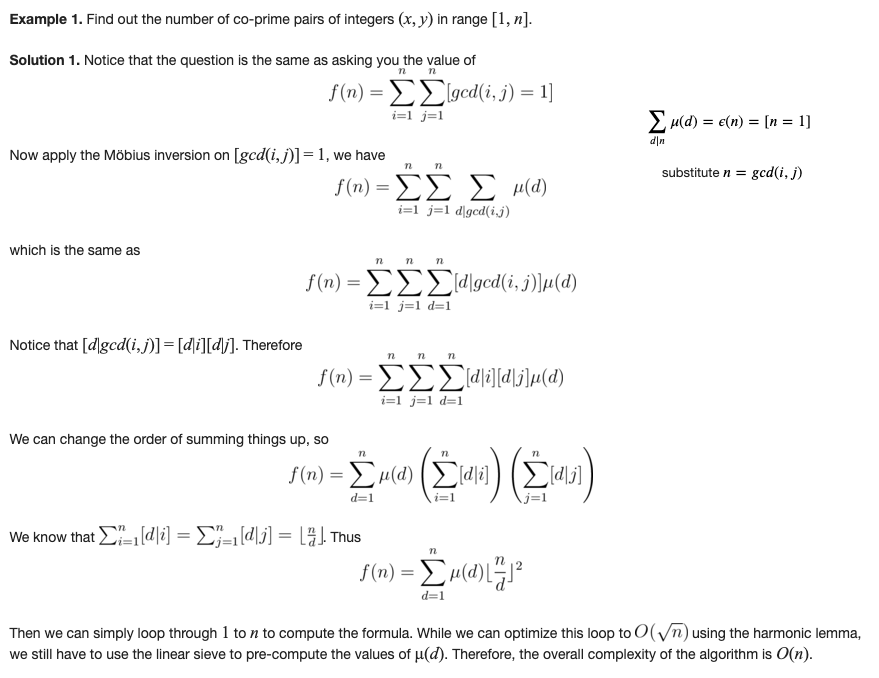



Example 5. Calculate GCD(1, 1) * GCD(1, 2) * ... * GCD(1, M) * GCD(2, 1) * GCD(2, 2) * ... * GCD(2, M) * ... * GCD(N, 1) * GCD(N, 2) * ... * GCD(N, M).
where GCD is defined as the Greatest Common Divisor.
https://www.hackerrank.com/contests/w3/challenges/gcd-product/problem
Solution

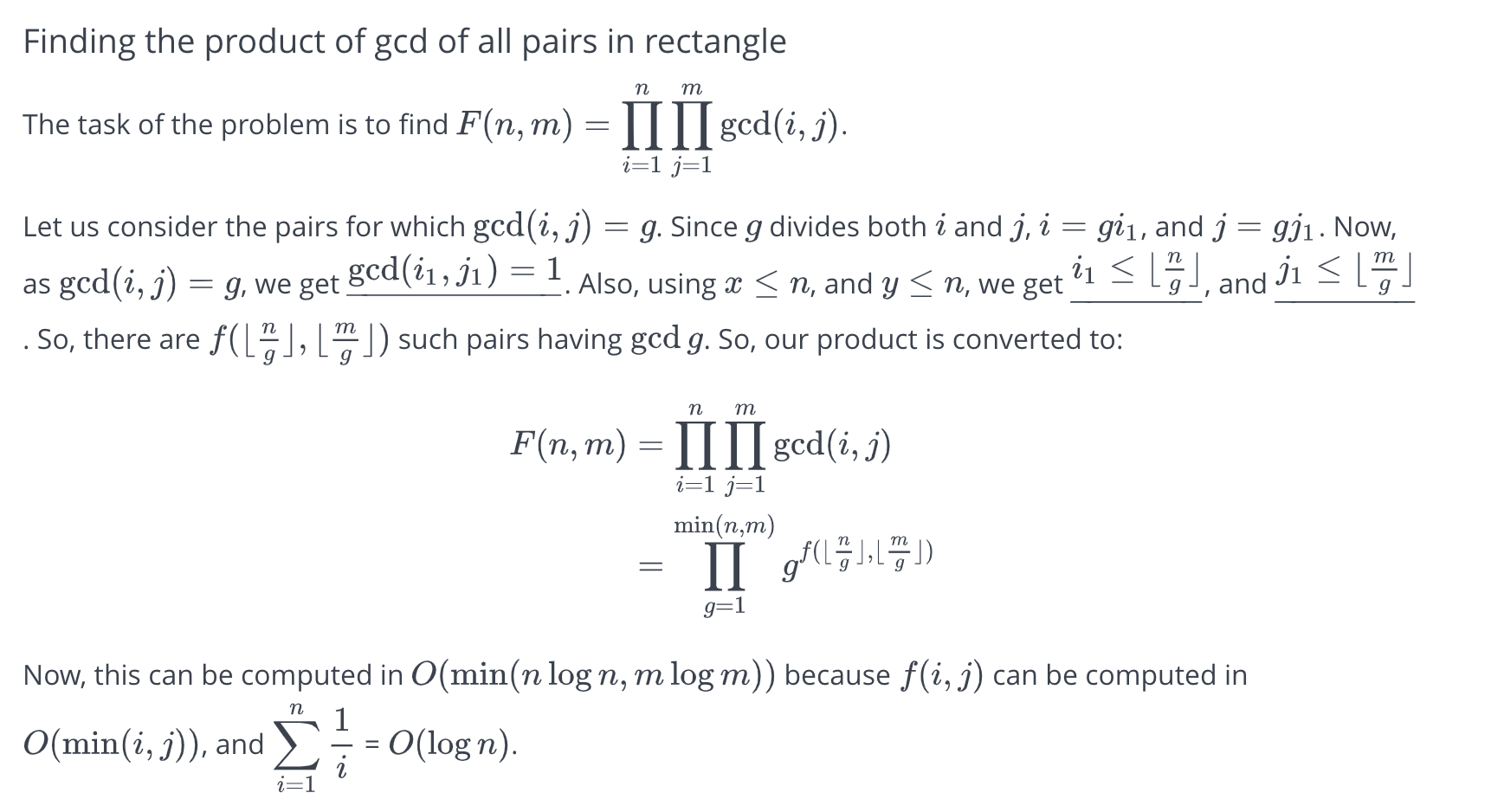
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 15000000 + 5
#define mod 1000000007
#define tm Tm
int n, m, i, j, p[maxn], dp[maxn], sf[maxn], sfn, g, tn, tm, ret, pref[maxn], l, c, p1, p2, r, carry;
long long sfm[maxn], t;
// binomial exponentiation
int pw (int x, long long p) {
if (!p) return 1;
if (p == 1) return x;
int q = pw(x, p >> 1);
q = (1LL * q * q) % mod;
if (p & 1) q = (1LL * q * x) % mod;
return q;
}
int main () {
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
if (n < m) swap(n, m);
// smallest prime factor of i = p[i]
for(i = 2; i <= n; i++) if (p[i] == 0) {
j = i;
while (j <= n) {
if (!p[j]) p[j] = i;
j += i;
}
}
for(i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
// mobius function -> dp[i]
if (i == p[i]) dp[i] = -1;
else if (p[(i / p[i])] == p[i]) dp[i] = 0; // if some prime^2 divides i
else dp[i] = -1 * dp[i / p[i]];
pref[i] = pref[i - 1] + dp[i];
}
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++) if (dp[i] != 0) {
sf[++sfn] = i; // square free number
sfm[sfn] = dp[i]; // mobius of square free number
}
sf[sfn + 1] = m + 1;
ret = 1;
carry = 1, t = 1, tn = tm = -1;
for(g = 2; g <= m; g++) {
if (n / g != tn || m / g != tm) {
ret = (ret * 1LL * pw(carry, t)) % mod;
carry = 1LL;
} else {
carry = (carry * 1LL * g) % mod;
continue;
}
tn = n / g;
tm = m / g;
t = 1LL * tn * tm;
if (g <= 600000) {
l = 1;
while (l <= tm) {
++c;
r = min(min(tn / (p1 = tn / l), tm / (p2 = tm / l)), tm);
// till r -> p1 & p2 doesn't change, hence use prefix sums for mobius function
t += p1 * 1LL * p2 * (pref[r] - pref[l - 1]);
l = r + 1;
}
// there are only 2*sqrt(max(n,m)) different values for p1 and p2
} else {
// brute force computation of f(tn, tm)
for(i = 1; sf[i] <= tm; i++)
t += sfm[i] * (tn / sf[i]) * (tm / sf[i]);
}
carry = (1LL * carry * g) % mod;
}
ret = (ret * 1LL * pw(carry, t)) % mod;
printf("%d\n", ret);
return 0;
}
Also checkout https://codeforces.com/blog/entry/8989?#comment-214114
Problem:

Property:
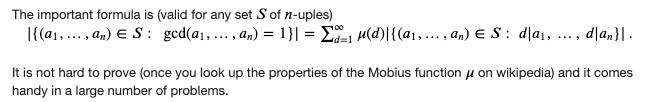
Solution:

const int nax = 1e5 + 10;
#define MOD 998244353
// modular int
struct mi {
int v; explicit operator int() const { return v; }
mi() { v = 0; }
mi(ll _v):v(_v%MOD) { v += (v<0)*MOD; }
};
mi& operator+=(mi& a, mi b) {
if ((a.v += b.v) >= MOD) a.v -= MOD;
return a; }
mi& operator-=(mi& a, mi b) {
if ((a.v -= b.v) < 0) a.v += MOD;
return a; }
mi operator+(mi a, mi b) { return a += b; }
mi operator-(mi a, mi b) { return a -= b; }
mi operator*(mi a, mi b) { return mi((ll)a.v*b.v); }
mi& operator*=(mi& a, mi b) { return a = a*b; }
mi pow(mi a, ll p) { assert(p >= 0); // asserts are important!
return p==0?1:pow(a*a,p/2)*(p&1?a:1); }
mi inv(mi a) { assert(a.v != 0); return pow(a,MOD-2); }
mi operator/(mi a, mi b) { return a*inv(b); }
int l[nax], r[nax]; // input
const int X = 1e5 + 10;
bitset<X> is_prime;
vector<int> pr;
int mu[nax];
// computing mu
void init() {
is_prime.flip();
is_prime[0] = is_prime[1] = false;
mu[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < X; i++) {
if (is_prime[i]) {
pr.push_back(i);
mu[i] = -1;
}
for (int p: pr) {
if (i * p >= X) break;
is_prime[i * p] = false;
if (i % p == 0) {
mu[i * p] = 0;
} else {
mu[i * p] = -mu[i];
}
if (i % p == 0) break;
}
}
}
int main() {
int n, m; scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d %d", &l[i], &r[i]);
init();
mi total = 0;
for(int d=1; d<=m; d++){
if(mu[d] == 0) continue;
// li/d <= ai <= ri/di
// Use Knapsack DP to find sum(ai) = m/d
int S = m/d + 1;
vector<mi> dp(S, 0);
dp[0] = 1;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
vector<mi> psum(S+1, 0); // prefix sums
for(int x=0; x<S; x++) psum[x+1] = psum[x] + dp[x];
int newl = (l[i] + d - 1)/d; // ceil of l[i]/d
int newr = r[i]/d; // floor of r[i]/d
vector<mi> ndp(S, 0);
if(newl <= newr){
for(int x = 0; x < S; x++){
// number of pairs such that a1 + a2 + ... + ai = x and newl <= ai <= newr
// a1 + a2 + ... + a(i-1) in between [x-newr, x-newl]
// sum[x - newl + 1] - sum[(x - newr + 1) - 1]
ndp[x] = psum[max(x - newl + 1, 0)] - psum[max(x - newr, 0)];
}
}
dp = ndp;
}
// find the dp sum to satisfy '<' condition
mi ans = 0;
for(mi v:dp) ans += v;
total += ans * mu[d];
}
printf("%d\n", (int)total);
return 0;
}
source: https://discuss.codechef.com/t/a-dance-with-mobius-function/11315 and https://codeforces.com/contest/1559/problem/E based on https://codeforces.com/blog/entry/93788?#comment-829004
REF: https://math.berkeley.edu/~stankova/MathCircle/Multiplicative.pdf