Notes
Given an arbitrary undirected graph, find the maximum number of pairs of edges such that each pair shares at least one endpoint and each edge is included in no more than one pair.

Example:
Input
7
4 1 5 1
1 1 1 1
3 3 3 3
1 1 4 1
6 1 1 1
5 1 4 1
6 1 1 1
Output
3
1 6
2 4
5 7
Here are the points and the moves for the ones that get chosen for the moves from the first example:
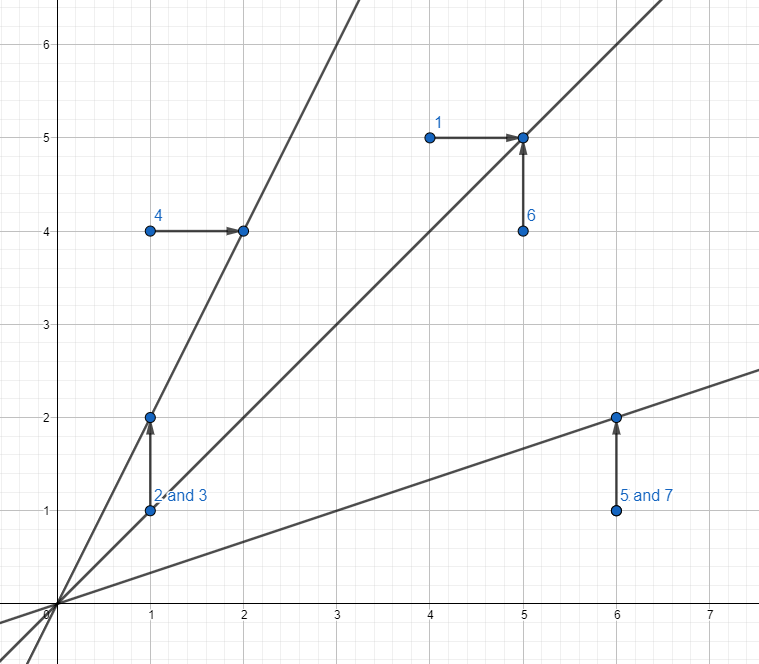
source: https://codeforces.com/contest/1519/problem/E

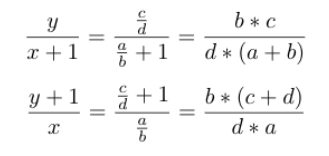
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <queue>
#include <ctime>
#include <cassert>
#include <complex>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <chrono>
#include <random>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
#ifdef LOCAL
#define eprintf(...) fprintf(stderr, __VA_ARGS__);fflush(stderr);
#else
#define eprintf(...) 42
#endif
using ll = long long;
using ld = long double;
using uint = unsigned int;
using ull = unsigned long long;
template<typename T>
using pair2 = pair<T, T>;
using pii = pair<int, int>;
using pli = pair<ll, int>;
using pll = pair<ll, ll>;
mt19937_64 rng(chrono::steady_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count());
ll myRand(ll B) {
return (ull)rng() % B;
}
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define all(x) (x).begin(),(x).end()
#define fi first
#define se second
clock_t startTime;
double getCurrentTime() {
return (double)(clock() - startTime) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
}
ll gcd(ll x, ll y) {
return y == 0 ? x : gcd(y, x % y);
}
map<pll, int> toId;
int n, m;
int getId(pll p) {
if (toId.count(p) == 0) {
toId[p] = n++;
}
return toId[p];
}
// normalise the point (x, y)
pll getFrac(ll x, ll y) {
ll g = gcd(x, y);
return mp(x / g, y / g);
}
const int N = 400200;
vector<int> g[N];
int ed[N][2];
bool used[N]; // to check whether dfs on some node is done
bool usedEd[N]; // to note whether some node is used
vector<pii> ans;
// get other end of the edge[id]
int getOther(int id, int v) {
return ed[id][0] ^ ed[id][1] ^ v;
}
bool dfs(int v, int par) {
used[v] = 1;
int lst = -1;
for (int id : g[v]) {
if (id == par) continue;
if (usedEd[id]) continue;
int u = getOther(id, v);
if (!used[u]) {
if (dfs(u, id)) continue;
}
usedEd[id] = true;
if (lst == -1) {
lst = id;
} else {
ans.push_back(mp(lst, id));
lst = -1;
}
}
if (lst != -1 && par != -1) {
usedEd[par] = true;
ans.push_back(mp(lst, par));
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
int main()
{
startTime = clock();
// freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout);
scanf("%d", &m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
ll a, b, c, d;
scanf("%lld%lld%lld%lld", &a, &b, &c, &d);
int v = getId(getFrac(c * b, d * (a + b)));
int u = getId(getFrac((c + d) * b, d * a));
ed[i][0] = v;
ed[i][1] = u;
g[v].push_back(i);
g[u].push_back(i);
}
for (int v = 0; v < n; v++) {
if (used[v]) continue;
dfs(v, -1);
}
printf("%d\n", (int)ans.size());
for (pii t : ans)
printf("%d %d\n", t.first + 1, t.second + 1);
return 0;
}
source: Um_nik https://codeforces.com/contest/1519/submission/114583294
Editorial Solution
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define forn(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < int(n); i++)
#define x first
#define y second
using namespace std;
struct point{
int a, b, c, d;
};
typedef pair<long long, long long> frac;
typedef pair<int, int> pt;
int n;
vector<point> a;
map<frac, int> sv;
frac norm(long long x, long long y){
long long g = __gcd(x, y);
return {x / g, y / g};
}
vector<vector<pt>> g;
vector<int> used;
vector<pt> ans;
int dfs(int v){
used[v] = 1;
int cur = -1;
for (auto it : g[v]){
int u = it.x;
int i = it.y;
if (used[u] == 1) continue;
int nw = i;
if (!used[u]){
int tmp = dfs(u);
if (tmp != -1){
ans.push_back({nw, tmp});
nw = -1;
}
}
if (nw != -1){
if (cur != -1){
ans.push_back({cur, nw});
cur = -1;
}
else{
cur = nw;
}
}
}
used[v] = 2;
return cur;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
a.resize(n);
forn(i, n) scanf("%d%d%d%d", &a[i].a, &a[i].b, &a[i].c, &a[i].d);
g.resize(2 * n);
forn(i, n){
frac f1 = norm((a[i].a + a[i].b) * 1ll * a[i].d, a[i].b * 1ll * a[i].c);
frac f2 = norm(a[i].a * 1ll * a[i].d, a[i].b * 1ll * (a[i].c + a[i].d));
if (!sv.count(f1)){
int k = sv.size();
sv[f1] = k;
}
if (!sv.count(f2)){
int k = sv.size();
sv[f2] = k;
}
g[sv[f1]].push_back({sv[f2], i});
g[sv[f2]].push_back({sv[f1], i});
}
used.resize(sv.size());
forn(i, sv.size()) if (!used[i])
dfs(i);
printf("%d\n", int(ans.size()));
for (auto it : ans) printf("%d %d\n", it.x + 1, it.y + 1);
}