Notes
TODO: https://codeforces.com/contest/1535/problem/F & https://codeforces.com/blog/entry/91481
Read from https://usaco.guide/PAPS.pdf#page=243
Strings - sequence of characters
String Algorithms
Pattern Searching - Given pattern(s) and text(s), we want to find all the occurences of patterns in the given text.
In C++, std::strstr() is a predefined function, which takes two strings s1 and s2 as an argument and finds the first occurrence of the sub-string s2 in the string s1.
char str[] = "Use your brain and heart";
char target[] = "brain";
char *p = strstr(str, target);
size_t find (const string& str, size_t pos = 0);
Function parameters:
str: The sub-string to be searched.s: The sub-string to be searched, given as C style string.pos: The initial position from where the string search is to begin.
Generally, the above mentioned algorithms use naive way of finding substrings which is O(n * m).
Preprocessing
Two different ways - Preprocess what you are searching for, or what you are searching in
Preprocess patterns
- 1 pattern & 1 text setup --> Z function, Prefix algorithm(KMP algorithm), Hashing
- 1 pattern & many texts --> KMP automaton, process pattern and search in texts in real time( 1 char of text will take 1 unit of time to process, unlike amortized complexity).
- KMP can be generalized to multiple pattern & multiple texts --> Aho Corasick automaton
- (multiple pattern & 1 text) --> Simple case of above setup
In the following we first preprocess text
- 1 text & multiple pattern --> Process texts before, allows us to search in time proportional to pattern not text, only text pre-processing takes time. Suffix structure -> Suffix arrays, suffix tree and suffix automaton. Can be generalized
- Multiple patterns & multiple texts --> Which you preprocess is important
Z-function
The Z-function for a string(of length n) is an array of length n where the i-th element is equal to the greatest number of characters starting from the position i that coincide with the first characters of s.
Function Z : {1,…,n-1} -> {0,…,n-1} such that Z[i] = max{ j: s[0..j-1] = s[i..i+j-1] }
In other words, Z[i] is equal to length of longest common prefix of s and s[i..n-1]. We can take Z[0] = 0. In some problems, it might be better if we use n instead of 0.
E.g: s = abacabc, gray strings(a, aba, abacaba ...) . Let's calculate Z function Z[0] = 0 (by def.), Z[1] = 0, Z[2] = 1.
To check running time of our algorithm, It's better if we check our string algorithm on such gray strings. If s = aaaaa then Z = [0, 4, 3, 2, 1]. When s = ababab then Z = [0, 0, 4, 0, 2, 0].
Applications:
- For pattern matching, say we are given pattern
pand textt, then we can compute Z-function ofp#tto find all the substrings that match withp.
Algorithm:
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
while (i + z[i] < n && s[z[i]] == s[i + z[i]]) ++z[i];
The above works but is too slow O(n^2).
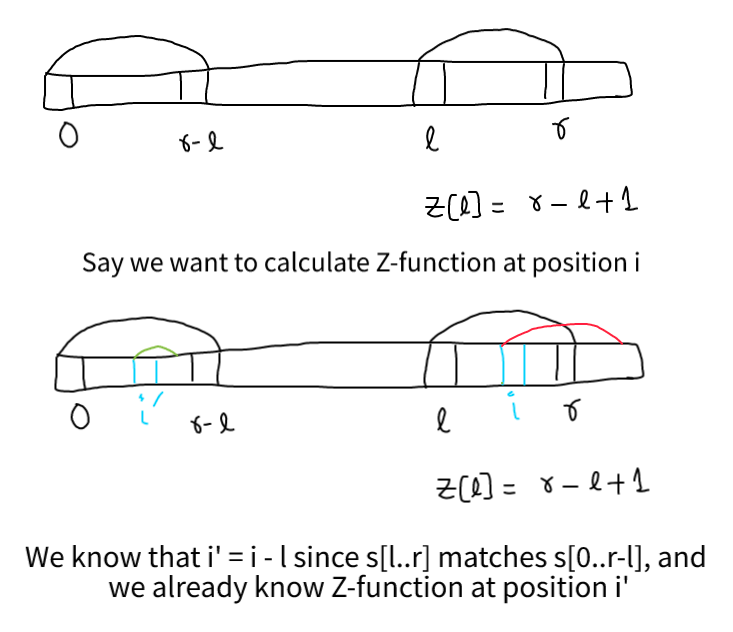
Consider a Z-block say L to R, which consists of current index i, then we can see that Z[i] can be R - i + 1 or Z[i-L]
L = R = 0
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i){
if (i <= R)
z[i] = min (R - i + 1, z[i - L]); // Initialization
while (i + z[i] < n && s[z[i]] == s[i + z[i]])
++z[i];
if (i + z[i] - 1 > R) L = i, R = i + z[i] - 1;
}
Initialization step Z[i] = min(), Z > R-i+1 is impossible to start, by definition of Z.
We can see that whenever the above while executes, R value increased and it can increase to at most n
Applications
- Now we can use this like this
pat$text, and this requiresO(m+n)time, wherem = |pat|andn = |text|andO(m)space and we no need to storez[i]for text, if we just want to find substring matching. - If we want to count number of different substrings of
s, says = abacaba,- there are
3substrings of length1-a,b,c; 4substrings of length2-ab,ba,ac,ca;4substrings of length 3 -aba,bac,aca,caband so on, there are total17different substrings.
- there are
- There are about
O(n^2)substrings and comparing two substrings can take uptoO(n)time, so naive algorithm can take uptoO(n^3)time. - We can use Z-function to solve this problem in
O(n^2)time. - Let's start with empty string and add one by one character and calculate the answer, for emtpy string
""- the answer is0, Let's add first charactera- the answer is1, let's addb, then our string isab- we get 3 =1(a) + 2 more (bandab); Forabcthe answer is6,3fromabandc,bcandabc. Let's considerabathen the answer is3+2 = 5. Whenever we add a letter to end, all the suffixes might increment the answer. Forabac- answer increments by4fromababecause all the suffixes are unique. For a given string, we want to find the longest suffix which has already appeared, all other suffixes will be the ones which we didn't see earlier. We can use Z-function to claclulate the longest suffix by first reversing the string and finding maximumZ[i].
- We can also find the total length of all different substrings.
- Search with atmost
1mistake, we have to pattern matching such that pattern differs in atmost1position. For examplet = abcabdababcand pattern =abaa, the answer isYes. We have to findp#t, ifZ[i] = len(p)then answer isYes, If not, we can use reverse of string and find Z-functionrev(p)#rev(t)and now use them to find the answer.
Prefix function (KMP algorithm)

Two observations: https://cp-algorithms.com/string/prefix-function.html
vector<int> prefix_function(string s) {
int n = (int)s.length();
vector<int> pi(n);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int j = pi[i-1];
while (j > 0 && s[i] != s[j])
j = pi[j-1];
if (s[i] == s[j])
j++;
pi[i] = j;
}
return pi;
}
Building an automaton according to the prefix function
Ref: https://codeforces.com/contest/1721/problem/E
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define forn(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < int(n); i++)
using namespace std;
const int AL = 26;
vector<int> prefix_function(const string &s){
int n = s.size();
vector<int> p(n);
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i){
int k = p[i - 1];
while (k > 0 && s[i] != s[k])
k = p[k - 1];
k += (s[i] == s[k]);
p[i] = k;
}
return p;
}
int main() {
cin.tie(0);
iostream::sync_with_stdio(false);
string s;
cin >> s;
int n = s.size();
auto p = prefix_function(s);
vector<vector<int>> A(n, vector<int>(AL));
forn(i, n) forn(j, AL){
if (i > 0 && j != s[i] - 'a')
A[i][j] = A[p[i - 1]][j];
else
A[i][j] = i + (j == s[i] - 'a');
}
int q;
cin >> q;
vector<vector<int>> ans(q);
forn(z, q){
string t;
cin >> t;
int m = t.size();
s += t;
for (int i = n; i < n + m; ++i){
A.push_back(vector<int>(AL));
forn(j, AL){
if (j != s[i] - 'a')
A[i][j] = A[p[i - 1]][j];
else
A[i][j] = i + (j == s[i] - 'a');
}
p.push_back(A[p[i - 1]][s[i] - 'a']);
ans[z].push_back(p[i]);
}
forn(_, m){
p.pop_back();
s.pop_back();
A.pop_back();
}
}
for (auto &it : ans){
for (int x : it)
cout << x << ' ';
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
Other string related problems
Length of the longest substring of s consisting of only one repeating character
Given a string s, we need to perform queries of the form:
The i-th query updates the character in s at index queryIndices[i] to the character queryCharacters[i].
Return an array lengths of length k where lengths[i] is the length of the longest substring of s consisting of only one repeating character after the ith query is performed.
Idea: We can store the string as segments of repeating characters. This way we can do queries efficiently. If we use segment trees(storing left and right sum for each character, we will get TLE).
vector<int> longestRepeating(string s, string queryCharacters, vector<int>& queryIndices) {
int n = s.size(), k = queryCharacters.size();
multiset<int> ms; // to store length of repeating subarray
set<pair<int, int> > sp; // store segments [a, b]
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < s.size(); i = j) {
while (j < s.size() and s[i] == s[j])
j += 1;
sp.emplace(i, j - 1);
ms.insert(j - i);
}
vector<int> res(k);
for (int i = 0; i < k; i += 1) {
int p = queryIndices[i];
char c = queryCharacters[i];
if (c != s[p]) {
auto pr = *prev(sp.upper_bound(make_pair(p, n)));
ms.erase(ms.find(pr.second - pr.first + 1));
sp.erase(pr);
if (pr.first < p) {
sp.emplace(pr.first, p - 1);
ms.insert(p - pr.first);
}
if (pr.second > p) {
sp.emplace(p + 1, pr.second);
ms.insert(pr.second - p);
}
s[p] = c;
int L = p, R = p;
if (p + 1 < n and s[p + 1] == c) {
auto it = sp.upper_bound(make_pair(p, n));
R = it->second;
ms.erase(ms.find(it->second - it->first + 1));
sp.erase(it);
}
if (p and s[p - 1] == c) {
auto it = prev(sp.upper_bound(make_pair(p, n)));
L = it->first;
ms.erase(ms.find(it->second - it->first + 1));
sp.erase(it);
}
sp.emplace(L, R);
ms.insert(R - L + 1);
}
res[i] = *ms.rbegin();
}
return res;
}
Similar idea to store segments or interval-sets https://codingcompetitions.withgoogle.com/kickstart/round/00000000008f49d7/0000000000bcf0fd#analysis
Solution:


Complete Code:
deltas = {
'N': (-1, 0),
'E': (0, 1),
'W': (0, -1),
'S': (1, 0)
}
reverse = {
'N': 'S', 'S': 'N', 'E': 'W', 'W': 'E'
}
def jump(jumps, i, row, col):
if jumps.get(i):
return jumps[i]
d_r, d_c = deltas[i]
return (row + d_r, col + d_c)
def add_jump(jumps, i, row, col):
d_r, d_c = deltas[i]
jumps[i] = (row + d_r, col + d_c)
def end_position(N, R, C, Sr, Sc, instructions):
table = {}
table[(Sr, Sc)] = {}
cur_r = Sr
cur_c = Sc
for i in instructions:
# from pprint import pprint
# print("DEBUG: ", i, cur_r, cur_c)
# pprint(table)
prev_r, prev_c = cur_r, cur_c
jumps_from_cur = table[(cur_r, cur_c)]
cur_r, cur_c = jump(table, i, cur_r, cur_c)
while table.get((cur_r, cur_c)):
jumps_from_cur = table[(cur_r, cur_c)]
cur_r, cur_c = jump(jumps_from_cur, i, cur_r, cur_c)
table[(cur_r, cur_c)] = {}
add_jump(table[(cur_r, cur_c)], reverse[i], prev_r, prev_c)
add_jump(table[(prev_r, prev_c)], i, cur_r, cur_c)
final_r, final_c = cur_r, cur_c
return final_r, final_c
def main():
test_cases = int(input())
for test_case in range(1, test_cases + 1):
N, R, C, Sr, Sc = map(int, input().split())
instructions = input()
# print(N, R, C, Sr, Sc, instructions)
final_r, final_c = end_position(N, R, C, Sr, Sc, instructions)
print(f'Case #{test_case}: {final_r} {final_c}')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
How it works with debug logs:
# Input
5 3 6 2 3
EEWNS
DEBUG: E 2 3
{(2, 3): {}}
DEBUG: E 2 4
{(2, 3): {'E': (2, 5)}, (2, 4): {'W': (2, 2)}}
DEBUG: W 2 5
{(2, 3): {'E': (2, 5)},
(2, 4): {'E': (2, 6), 'W': (2, 2)},
(2, 5): {'W': (2, 3)}}
DEBUG: N 2 2
{(2, 2): {'E': (2, 6)},
(2, 3): {'E': (2, 5)},
(2, 4): {'E': (2, 6), 'W': (2, 2)},
(2, 5): {'W': (2, 1)}}
DEBUG: S 1 2
{(1, 2): {'S': (3, 2)},
(2, 2): {'E': (2, 6), 'N': (0, 2)},
(2, 3): {'E': (2, 5)},
(2, 4): {'E': (2, 6), 'W': (2, 2)},
(2, 5): {'W': (2, 1)}}
# Output
Case #1: 3 2
GCD of two strings
or two strings s and t, we say "t divides s" if and only if s = t + ... + t (i.e., t is concatenated with itself one or more times).
Given two strings str1 and str2, return the largest string x such that x divides both str1 and str2.
Ref: https://leetcode.com/problems/greatest-common-divisor-of-strings/description/
string gcdOfStrings(string str1, string str2) {
int a = str1.size(), b = str2.size(), g = __gcd(a, b);
if(str1 + str2 == str2 + str1) return str1.substr(0, g);
return "";
}